[ad_1]
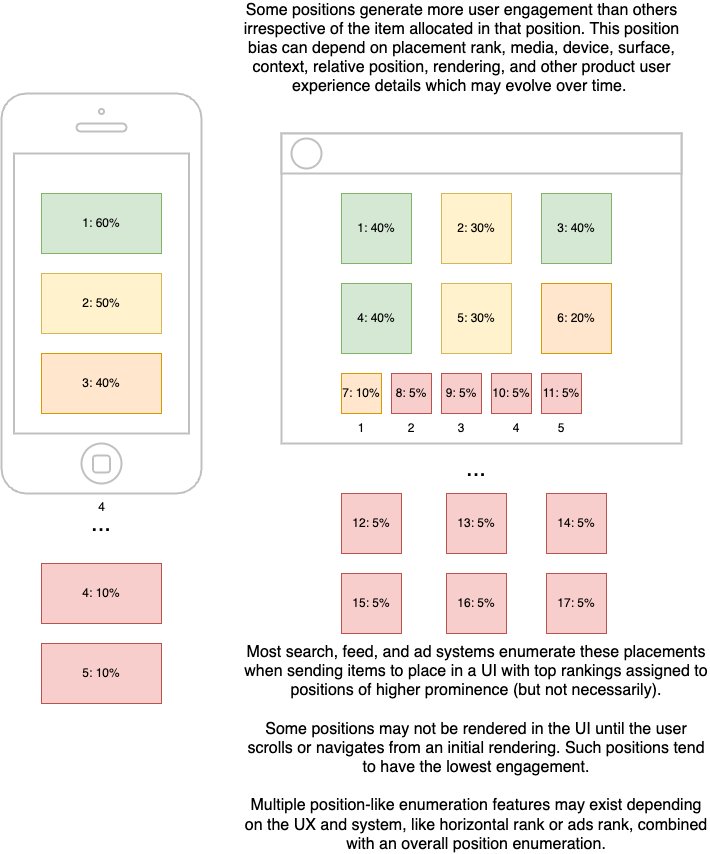
“Position Bias” in search, feed, and ads ranking is when the probability of engagement, like a click, is confounded by a bias from where the item was shown in the past. Generally, the top ranks are more engaging. Items allocated to the top get more engagement regardless of how good that item was for that allocation. Because engagement models learn from past engagement models, this can result in a bias where past winners always remain winners, and the model can never learn otherwise.
In ads ranking, position bias also impacts ad pricing when auction prices depend on the bids for multiple positions in an allocation. In general, for GSP and VCG ad auctions, uncorrected position bias tends to inflate prices for top positions because the value of lower, less valuable positions is relatively overestimated.
Promoted.ai has many methods for handling position bias to ensure we model and deliver the best, most valuable experience in search, feed, and ads rankings.
Bias Correction Methods:
- Eventing
- L2 Machine Learning Feature Design
- L2 Model Architecture
- Offline Evaluation of L2 Models with Bias Correction
- Metrics and Counters
- L3 Model Design
Visibility Eventing in p(click) modeling
The most common and extreme position bias results when an allocation position is likely never presented to a user. If the item allocated to a position is never presented to a user, it can never generate engagement. An engagement model is typically used to estimate “quality,” which assumes presentation to the user. An engagement model where some negative examples are never presented to users, especially when the likelihood of presentation to users is influenced by past engagement modeling, generates a spurious negative bias.
Promoted logs impressions using IAB visibility standards and uses impressions as negative examples in our p(click) models, not server-side insertions.
Post-Click Modeling
A second way Promoted uses eventing to address position bias is post-click modeling, where all training examples are clicks, and the labels are some user engagement after a click. Once a user has clicked or navigated to a list item, the allocation position’s impact on additional, more highly considered user behavior like “purchase” is largely mitigated because the user has already decided to select that item. This “Markov model” of user engagement isolates the impact of position on the impression-to-click model. Because most of the position bias is mitigated by the design post-click models, the post-click model fits using other non-position-bias features that are more likely to model the actual quality of the item for this user in this context after sufficient user consideration. We can observe this effect by including allocation position in post-click models and confirming that the allocation position is not an important feature for these models.
Allocation Position Features
Some features, like “position,” are used in training but set to 0 at inference time. This is because the feature value depends on the allocation, which isn’t known at the time of L2 inference. (In multi-stage search and ads ranking, L2 is a reranking of the top K results from a retrieval system where K is typically about ≤1,000). There may be multiple “allocation position” features, like overall position, carousel position, relative page position, horizontal position, ads rank position, etc. All such features are handled similarly: set for training to model position bias but set to 0 at L2 inference time.
In effect, this models the impact of the position feature in training and subtracts its bias at inference. This is similar in concept to “batch effect correction” techniques used in other sciences. Furthermore, the top position tends to be the most commonly sampled in training data, so engagement at the top position is the most well-modeled compared to any other position.
Context Features
The allocation position alone may not provide enough information to model the impact of position bias if different devices, surfaces, and displays are combined in the training set. To add this context, we include context features like device type, page size, and product surface and model the impact of the position feature in interaction with these context features.
Exclusion of Retrieval Features During Installation
Promoted sometimes uses the retrieval score or rank as a ranking feature in L2 second-stage ranking. However, when adding a new L2 second-stage model on top of a traditional L1 search ranking system, the retrieval rank and score are proxies for the allocation position in the existing system. That is, the retrieval rank and score exactly or nearly exactly represent the allocation position. Using retrieval score and rank in this case can circumvent other special treatments we use to correct position bias.
When training on data generated by the existing system, particularly when bootstrapping a new L2 ranking system, we exclude retrieval score and rank as features in L2 ranking models. Later, after deploying the L2 and decoupling the direct relationship between retrieval score and rank and allocation position, we sometimes add retrieval ranks and scores back as L2 ranking features if that significantly improves L2 model fit. Sometimes, this is because our customers do custom modeling to generate retrieval scores on data Promoted cannot easily access, like domain-level computation of term-frequency as used in computing BM25 scores commonly used as an L1 ranking score.
When including allocation position as a feature in ranking models, we often observe that the model overfits on the allocation position, particularly for p(click|impression) models, at the exclusion of other features. This is partly because of allocation position bias, but it is also because of a confounding bias that high engagement probability items are likely allocated in first positions, and past delivery generates future training data. The result is a model that overfits to a signal of “goodness,” the position as decided by a past model, that isn’t available at inference time. This wastes model complexity and results in poor performance.
To mitigate this impact, we fit a combination of model architectures that include and exclude the allocation features in different layers. For example, we remove the position feature from GBDT component or dense connected NN component. Instead, we concatenate position feature along with other numerical features (optional) at different neural network layers.
Generally, while we use autoML to find ideal model architectures depending on the domain, customer, and data volume, we find that Neural Network (NN) architectures outperform GBDT alone when accounting for position bias, even at medium data volumes where GBDTs tend to perform better than NN on position biased data. This may be because the discreet “branching” of GBDT causes all splits on the position feature to be discarded at inference when position is set to 0, thereby wasting considerable model complexity never used at inference time. NN can model a continuous relationship with position and does not have this issue.
Ideally, the impact of position bias correction is measured using live A/B testing data where users can react differently to different allocation positions. However, this may be infeasible, and an offline model evaluation metric is still desirable to demonstrate a mechanistic improvement in model performance before spending resources to collect A/B testing results. However, evaluation data generated from past delivery data will have biased labels from the position bias, making it challenging to measure improvements in correcting the position bias with that data. We used offline evaluation techniques to estimate improvements from correcting position bias.
Biased data set
[V1] click/impression data with allocation position as feature in both training and evaluation sets. This is the standard hold-out validation data used in most L2 model training without correction.
- Pros: Align with training data, where position is used as features
- Cons: Does not align with inference distribution, where position = 0. Uncorrected position bias performs best on V1, so using V1 to estimate the positive impact of position correction is challenging.
Unbiased data set [Estimation of the true data set]
[V2] full click/impression data, set position = 0 in evaluation
- Pros: Consistent with the inference distribution where the position is set to 0. No distortion for position = 0 in evaluation.
- Cons: User responses and therefore evaluation labels are still biased by position
[V3] Subset of impression with attributed conversions only, set position = 0
- Pros: Consistent with the inference distribution where the position is set to 0. No distortion for position = 0 in evaluation. An attributed conversion could indicate true matching intent regardless of allocation position.
- Cons: Very small subset evaluation data makes measurement noisy, attributed conversion bias correction assumption may not be correct.
[V4] click/impression data with real position = 0, other positions are discarded
- Pros: Consistent with the inference distribution where the position is set to 0. No evaluation data are distorted.
- Cons: Small subset of evaluation data. Does not directly test the impact of position on inference.
Average engagement rates are potent predictors of future engagement. However, the same bias in engagement labels applies to engagement features, too. Counter features and related measurements like average click-through rate (CTR) are also affected by position bias. This bias reduces the reliability of counter features, resulting in worse model fits and lower production impact.
For example, suppose an item is consistently delivered in the first position, and there is a strong position bias that items in the first position are likelier to be clicked regardless of the items allocated to the first position. In that case, CTR counter features computed using clicks for that item will be inflated compared to those calculated for items typically delivered in lower positions.
We correct this bias by computing the average engagement rate per position in a context (e.g., iOS position 1, 2, 3… web position 1, 2, 3… etc.) and generating “position bias-corrected” engagement rate counter features and metrics. Generally, positions with lower engagement rates “count more,” while positions with higher engagement rates “count less” in aggregate metrics and ratios.
Position-engagement Weighted Impressions
For CTR counter features, we correct the impression denominator by making impressions weigh more proportionally to how biased that position is towards engagement compared to a global engagement rate for the context. This allows us to easily compute aggregate sums of weighted impressions for all real-time engagement ratio counter features use using impressions. That is:
Rather than counting Impressions 1 by 1 for each, count for an impression at position “i” in a context, for example, iOS, count: CTR@pos(i,iOS)/CTR(allPositions,iOS)
If the position bias for position i is higher than the average (e.g., for position 1), then this impression will count for more than 1. The ratio will be proportionally lower when this weighted impression is used as a denominator in an average CTR counter feature sum(clicks) / sum(weighted impressions). Likewise, the ratio will be proportionally higher for impressions in low positions with less than average CTR.
For streaming efficiency, the position bias can be computed as a table published daily in a recurring data pipeline and saved in memory in a standard streaming accumulator using a system like Flink.
Position Bias Corrected Engagement Metrics
For some experiments, like ad load tuning, changing ad slot positions can change the click rates. This complicates typical A/B quality measures, like CTR, clicks, and ad revenue, if ad revenue includes cost-per-click billing. Generally, ad slots in higher positions will inflate click-related metrics, so such metrics cannot be reliably used to measure user experience quality.
Similar to impressions with engagement weights, weigh engagements like clicks by the inverse position engagement, so that higher, more engaging positions count less and vice versa. For example, for a click iOS in position i, weigh it by: CTR(allPositions,iOS)/CTR@pos(i,iOS)
Past position counter features
Counter features can also accumulate allocated position itself to learn corrections for position bias inherent in past data. At Promoted, we recommend accumulating the impression log-transformed allocation position transformed with dimensions for different product surfaces (search, home page, related products) and devices (iOS, web, mobile web). Add this feature to all ordinary engagement models in combination with allocation position features and historical engagement features and labels to learn a contextual correction of past delivery allocation position patterns to predict future delivery.
“L3” ranking is any allocation system where the priority method includes a dependency on each allocation position. For engineers familiar with Meta-style organic and ads ranking, these systems were typically the “Newsfeed ranking” and “prediction calibration” systems. “L2” is more similar to the AdFinder system, which traditionally computed predictions for items in a position and allocation-independent way. L3 systems typically use the L2 scores as features and models using features computed from allocation positions and other items in the allocation.
Non-mutating “Calibration” models
These adjustments do not change the allocation. Instead, they are used in ads ranking to correct (typically lower) event predictions in lower position to improve ad auction pricing performance (typically, lower prices and help the auction behave more similarly to a bid-your-true-value dominant strategy auction)
Promoted can use three types of non-mutating calibration models to improve pricing performance for ads:
- A simple “position curve” fixed multiple, like 100%, 90%, 70%, 60%, 50%, 50%, …
- A model with position and some context as features. This is similar to the position curve, but regularly trained on historical per-position miscalibrations between predictions at position 0 and observed events at an allocated position in a context.
- A real-time pacing system to force the average calibration per item to be near 100% for small windows of time, like an hour, as a correction to the pCTR model as compared to streaming measurement. This can also help mitigate the production impact of ML production failures that result in much too high or too low predictions that cause over and under-delivery of content.
Whole Page Optimization
Whole page optimization, slate learning, and sequence learning all use techniques of recomputing model inferences for every position. This is a complex topic and beyond the scope of merely handling positions in allocation. Generally, because inference is recomputed for each allocation position, the allocated position is available as a feature, and position bias is modeled directly. Additional after-allocation calibration corrections may still be applied even when directly modeling and computing inferences for each position to align allocation-attribution outcome measurements with per-item inferences.
[ad_2]