Choosing the right large language model (LLM) for your use case is becoming both increasingly challenging and essential. Many teams rely on one-time (ad hoc) evaluations based on limited samples from trending models, essentially judging quality on “vibes” alone.
This approach involves experimenting with a model’s responses and forming subjective opinions about its performance. However, relying on these informal tests of model output is risky and unscalable, often misses subtle errors, overlooks unsafe behavior, and provides no clear criteria for improvement.
A more holistic approach entails evaluating the model based on metrics around qualitative and quantitative aspects, such as quality of response, cost, and performance. This also requires the evaluation system to compare models based on these predefined metrics and give a comprehensive output comparing models across all these areas. However, these evaluations don’t scale effectively enough to help organizations take full advantage of the model choices available.
In this post, we discuss an approach that can guide you to build comprehensive and empirically driven evaluations that can help you make better decisions when selecting the right model for your task.
From vibes to metrics and why it matters
Human brains excel at pattern-matching, and models are designed to be convincing. Although a vibes-based approach can serve as a starting point, without systematic evaluation, we lack the evidence needed to trust a model in production. This limitation makes it difficult to compare models fairly or identify specific areas for improvement.
The limitations of “just trying it out” include:
- Subjective bias – Human testers might favor responses based on style or tone rather than factual accuracy. Users can be swayed by “exotic words” or formatting. A model whose writing sounds confident might win on vibes while actually introducing inaccuracies.
- Lack of coverage – A few interactive prompts won’t cover the breadth of real-world inputs, often missing edge cases that reveal model weaknesses.
- Inconsistency – Without defined metrics, evaluators might disagree on why one model is better based on different priorities (brevity vs. factual detail), making it difficult to align model choice with business goals.
- No trackable benchmarks – Without quantitative metrics, it’s impossible to track accuracy degradation during prompt optimization or model changes.
Established benchmarks like MMLU, HellaSwag, and HELM offer valuable standardized assessments across reasoning, knowledge retrieval, and factuality dimensions, efficiently helping narrow down candidate models without extensive internal resources.
However, exclusive reliance on these benchmarks is problematic: they measure generalized rather than domain-specific performance, prioritize easily quantifiable metrics over business-critical capabilities, and can’t account for your organization’s unique constraints around latency, costs, and safety requirements. A high-ranking model might excel at trivia while failing with your industry terminology or producing responses too verbose or costly for your specific implementation.
A robust evaluation framework is vital for building trust, which is why no single metric can capture what makes an LLM response “good.” Instead, you must evaluate across multiple dimensions:
- Accuracy – Does the model produce accurate information? Does it fully answer the question or cover required points? Is the response on-topic, contextually relevant, well-structured, and logically coherent?
- Latency – How fast does the model produce a response? For interactive applications, response time directly impacts user experience.
- Cost-efficiency – What is the monetary cost per API call or token? Different models have varying pricing structures and infrastructure costs.
By evaluating along these facets, you can make informed decisions aligned with product requirements. For example, if robustness under adversarial inputs is crucial, a slightly slower but more aligned model might be preferable. For simple internal tasks, trading some accuracy for cost-efficiency might make sense.
Although many metrics require qualitative judgment, you can structure and quantify these with careful evaluation methods. Industry best practices combine quantitative metrics with human or AI raters for subjective criteria, moving from “I like this answer more” to “Model A scored 4/5 on correctness and 5/5 on completeness.” This detail enables meaningful discussion and improvement, and technical managers should demand such accuracy measurements before deploying any model.
Unique evaluation dimensions for LLM performance
In this post, we make the case for structured, multi-metric assessment of foundation models (FMs) and discuss the importance of creating ground truth as a prerequisite to model evaluation. We use the open source 360-Eval framework as a practical, code-first tool to orchestrate rigorous evaluations across multiple models and cloud providers.
We show the approach by comparing four LLMs within Amazon Bedrock, across a spectrum of correctness, completeness, relevance, format, coherence, and instruction following, to understand how each model responds matches our ground truth dataset. Our evaluation measures the accuracy, latency, and cost for each model, painting a 360° picture of their strengths and weaknesses.
To evaluate FMs, it’s highly recommended that you break up model performance into distinct dimensions. The following is a sample set of criteria and what each one measures:
- Correctness (accuracy) – The factual accuracy of the model’s output. For tasks with a known answer, you can measure this using exact match or cosine similarity; for open-ended responses, you might rely on human or LLM judgment of factual consistency.
- Completeness – The extent to which the model’s response addresses all parts of the query or problem. In human/LLM evaluations, completeness is often scored on a scale (did the answer partly address or fully address the query).
- Relevance – Measures if the content of the response is on-topic and pertinent to the user’s request. Relevance scoring looks at how well the response stays within scope. High relevance means the model understood the query and stayed focused on it.
- Coherence – The logical flow and clarity of the response. Coherence can be judged by human or LLM evaluators, or approximated with metrics like coherence scores or by checking discourse structure.
- Following instructions – How well the model obeys explicit instructions in the prompt (formatting, style, length, and so on). For example, if asked “List three bullet-point advantages,” does the model produce a three-item bullet list? If the system or user prompt sets a role or tone, does the model adhere to it? Instruction-following can be evaluated by programmatically checking if the output meets the specified criteria (for example, contains the required sections) or using evaluator ratings.
Performing such comprehensive evaluations manually can be extremely time-consuming. Each model needs to be run on many if not hundreds of prompts, and each output must be checked for across all metrics. Doing this by hand or writing one-off scripts is error-prone and doesn’t scale. In practice, these can be evaluated automatically using LLM-as-a-judge or human feedback. This is where evaluation frameworks come into play.
After you’ve chosen an evaluation philosophy, it’s wise to invest in tooling to support it. Instead of combining ad hoc evaluation scripts, you can use dedicated frameworks to streamline the process of testing LLMs across many metrics and models.
Automating 360° model evaluation with 360-Eval
360-Eval is a lightweight solution that captures the depth and breadth of model evaluation. You can use it as an evaluation orchestrator to define the following:
- Your dataset of test prompts and respective golden answers (expected answers or reference outputs)
- Models you want to evaluate
- The metrics and tasks framework evaluating the models against
The tool is designed to capture relevant and user-defined dimensions of model performance in one workflow, supporting multi-model comparisons out of the box. You can evaluate models hosted in Amazon Bedrock or Amazon SageMaker, or call external APIs—the framework is flexible in integrating different model endpoints. This is ideal for a scenario where you might want to use the full power of Amazon Bedrock models without having to sacrifice performance.
The framework consists of the following key components:
- Data configuration – You specify your evaluation dataset; for example, a JSONL file of prompts with optional expected outputs, the task, and a description. The framework can also work with a custom prompt CSV dataset you provide.
- API gateway – Using the versatile LiteLLM framework, it abstracts the API differences so the evaluation loop can treat all models uniformly. Inference metadata such as time-to-first-token (TTFT), time-to-last-token (TTLT), total token output, API errors count, and pricing is also captured.
- Evaluation architecture – 360-Eval uses LLM-as-a-judge to score and calculate the weight of model outputs on qualities like correctness or relevance. You can provide all the metrics you care about into one pipeline. Each evaluation algorithm will produce a score and verdict per test case per model.
Choosing the right model: A real-world example
For our example use case, AnyCompany is developing an innovative software as a service (SaaS) solution that streamlines database architecture for developers and businesses. Their platform accepts natural language requirements as input and uses LLMs to automatically generate PostgreSQL-specific data models. Users can describe their requirements in plain English—for example, “I need a cloud-based order management platform designed to streamline operations for small to medium businesses”—and the tool intelligently extracts the entity and attribute information and creates an optimized table structure specifically for PostgreSQL. This solution avoids hours of manual entity and database design work, reduces the expertise barrier for database modeling, and supports PostgreSQL best practices even for teams without dedicated database specialists.
In our example, we provide our model a set of requirements (as prompts) relevant to the task and ask it to extract the dominant entity and its attributes (a data extraction task) and also produce a relevant create table statement using PostgreSQL (a text-to-SQL task).
Example prompt:
The following table shows our task types, criteria, and golden answers for this example prompt. We have shortened the prompt for brevity. In a real-world use case, your requirements might span multiple paragraphs.
| task_type | task_criteria | golden_answer |
DATA EXTRACTION | Check if the extracted entity and attributes matches the requirements | |
TEXT-TO-SQL | Given the requirements check if the generated create table matches the requirements |
AnyCompany wants to find a model that will solve the task in the fastest and most cost-effective way, without compromising on quality.
360-Eval UI
To reduce the complexity of the process, we have built a UI on top of the evaluation engine.
The UI_README.md file has instructions to launch and run the evaluation using the UI. You must also follow the instructions in the README.md to install the Python packages as prerequisites and enable Amazon Bedrock model access.
Let’s explore the different pages in the UI in more detail.
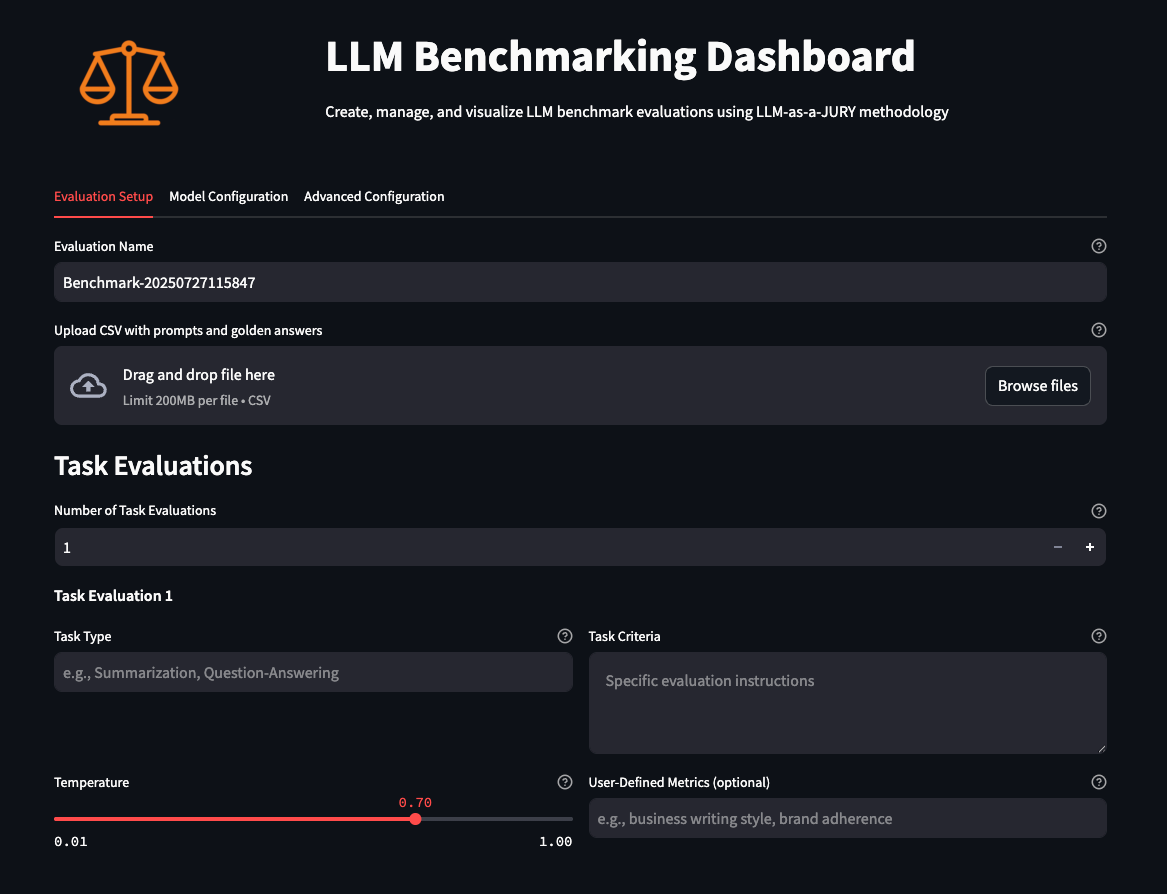
Setup page
As you launch the UI, you land on the initial Setup page, where you select your evaluation data, define your label, define your task as discreetly as possible, and set the temperature the models will have when being evaluated. Then you select the models you want to evaluate against your dataset, the judges that will evaluate the models’ accuracy (using custom metrics and the standard quality and relevance metrics), configure pricing and AWS Region options, and finally configure how you want the evaluation to take place, such as concurrency, request per minute, and experiment counts (unique runs).

This is where you specify the CSV file with sample prompts, task type, and task criteria according to your needs.
Monitor page
After the evaluation criteria and parameters are defined, they are displayed on the Monitor page, which you can navigate to by choosing Monitor in the Navigation section. On this page, you can monitor all your evaluations, including those currently running, those queued, and those not yet scheduled to run. You can choose the evaluation you want to run, and if any evaluation is no longer relevant, you can remove it here as well.
The workflow is as follows:
- Execute the prompts in the input file against the models selected.
- Capture the metrics such as input token count, output token count, and TTFT.
- Use the input and output tokens to calculate the cost of running each prompt against the models.
- Use an LLM-as-a-judge to evaluate the accuracy against predefined metrics (correctness, completeness, relevance, format, coherence, following instructions) and any user-defined metrics.

Evaluations page
Detailed information of the evaluations, such as the evaluation configuration, the judge models used to evaluate, the Regions where the models are hosted, the input and output cost, and the task and its criteria the model was evaluated with, are displayed on the Evaluations page.

Reports page
Lastly, the Reports page is where you can select the completed evaluations to generate a report in HTML format. You can also delete old and irrelevant reports.

Understanding the evaluation report
The tool output is an HTML file that shows the results of the evaluation. It includes the following sections:
- Executive Summary – This section provides an overall summary of the results. It provides a quick summary of which model was most accurate, which model was the fastest overall, and which model provided the best success-to-cost ratio.
- Recommendations – This section contains more details and a breakdown of what you see in the executive summary, in a tabular format.
- Latency Metrics – In this section, you can review the performance aspect of your evaluation. We use the TTFT and output tokens per second as a measure for performance.
- Cost Metrics – This section shows the overall cost of running the evaluation, which indicates what you can expect in your AWS billing.
- Task Analysis – The tool further breaks down the performance and cost metrics by task type. In our case, there will be a section for the text-to-SQL task and one for data extraction.
- Judge Scores Analysis – In this section, you can review the quality of each model based on the various metrics. You can also explore prompt optimizations to improve your model. In our case, our prompts were more biased towards the Anthropic family, but if you use the Amazon Bedrock prompt optimization feature, you might be able to address this bias.
Interpreting the evaluation results
By using the 360-Eval UI, AnyCompany ran the evaluation with their own dataset and got the following results. They chose four different LLMs in Amazon Bedrock to conduct the evaluation. For this post, the exact models used aren’t relevant. We call these models Model-A, Model-B, Model-C, and Model-D.
These results will vary in your case depending on the dataset and prompts. The results here are a reflection of our own example within a test account. As shown in the following figures, Model-A was the fastest, followed by Model-B. Model-C was 3–4 times slower than Model-A. Model-D was the slowest.


As shown in the following figure, Model B was the cheapest. Model A was three times more expensive than Model-B. Model-C and Model-D were both very expensive.

The next focus was the quality of the evaluation. The two most important metrics to were the correctness and completeness of the response. In the following evaluation, only Model-D scored more than 3 for both task types.

Model-C was the next closest contender.

Model-B scored lowest in the correctness and completeness metrics.

Model-A missed slightly on the completeness for the text-to-SQL use case.

Evaluation summary
Let’s revisit AnyCompany’s criteria, which was to find a model that will solve the task in the fastest and most cost-effective way, without compromising on quality. There was no obvious winner.
AnyCompany then considered providing a tiered pricing model to their customers. Premium-tier customers will receive the most accurate model at a premium price, and basic-tier customers will get the model with the best price-performance.
Although for this use case, Model-D was the slowest and more expensive, it scored highest on the most crucial metrics: correctness and completeness of responses. For a database modeling tool, accuracy is far more important than speed or cost, because incorrect database schemas might lead to significant downstream issues in application development. AnyCompany chose Model-D for premium-tier customers.
Cost is a major constraint for the basic-tier, so AnyCompany chose Model-A, because it scored reasonably well on correctness for both tasks and only slightly missed on completeness for one task type, while being faster and less expensive than the top performers.
AnyCompany also considered Model-B as a viable option for free-tier customers.
Conclusion
As FMs become more reliant, they can also become more complex. Because their strengths and weaknesses more difficult to detect, evaluating them requires a systematic approach. By using a data-driven, multi-metric evaluation, technical leaders can make informed decisions rooted in the model’s actual performance, including factual accuracy, user experience, compliance, and cost.
Adopting frameworks like 360-Eval can operationalize this approach. You can encode your evaluation philosophy into a standardized procedure, making sure every new model or version is judged the same, and enabling side-by-side comparisons.
The framework handles the heavy lifting of running models on test cases and computing metrics, so your team can focus on interpreting results and making decisions. As the field of generative AI continues to evolve rapidly, having this evaluation infrastructure can help you find the right model for your use case. Furthermore, this approach can enable faster iteration on prompts and policies, and ultimately help you develop more reliable and effective AI systems in production.
About the authors
 Claudio Mazzoni is a Sr Specialist Solutions Architect on the Amazon Bedrock GTM team. Claudio exceeds at guiding costumers through their Gen AI journey. Outside of work, Claudio enjoys spending time with family, working in his garden, and cooking Uruguayan food.
Claudio Mazzoni is a Sr Specialist Solutions Architect on the Amazon Bedrock GTM team. Claudio exceeds at guiding costumers through their Gen AI journey. Outside of work, Claudio enjoys spending time with family, working in his garden, and cooking Uruguayan food.
 Anubhav Sharma is a Principal Solutions Architect at AWS with over 2 decades of experience in coding and architecting business-critical applications. Known for his strong desire to learn and innovate, Anubhav has spent the past 6 years at AWS working closely with multiple independent software vendors (ISVs) and enterprises. He specializes in guiding these companies through their journey of building, deploying, and operating SaaS solutions on AWS.
Anubhav Sharma is a Principal Solutions Architect at AWS with over 2 decades of experience in coding and architecting business-critical applications. Known for his strong desire to learn and innovate, Anubhav has spent the past 6 years at AWS working closely with multiple independent software vendors (ISVs) and enterprises. He specializes in guiding these companies through their journey of building, deploying, and operating SaaS solutions on AWS.